

11. Atomically-controlled graphene nanostructures and ribbons:
Contact person:
Elisa Molinari
Deborah Prezzi
On-surface synthesis has been recently demonstrates a powerful approach to produce a
whole set of different organic nanostructures, opening the way to atomic-level design of
graphene-based nanodevices. This approach, which is feasible to be extended to CVD
growth conditions, allows in particular the complete control on size, edge termination, shape
and heteroatomic doping of graphene nanoribbons (GNR), which can be used as building
blocks for complex nanostructures and heterojuctions with foreseeable room-temperature
digital-logic applications. This activity aims at investigating the growth mechanisms, electronic
(band dispersions, excitons and plasmons) and vibrational properties of GNR-based
nanostructures, both grown in ultra-high-vacuum conditions and by CVD. Tailoring of the
nanostructure electronic and magnetic properties will be pursued by exploiting different
precursor molecules and by interaction with other organic and inorganic moieties (dopants,
magnetic species).
|
|
|
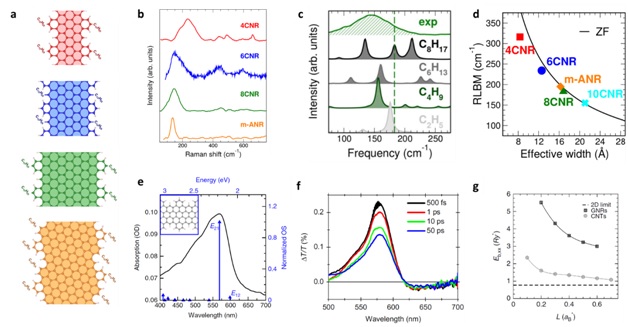
Comparison of Ramanand HREEL spectroscopy
with ab-initio simulations shows that GNR width, edge and termination morphology, and
functional groups, influence the GNR vibrational properties.
I. Verzhbitskiy, M. De
Corato, A. Ruini, E. Molinari, A. Narita, Y. Hu, M. G. Schwab, M. Bruna, D. Yoon, S.
Milana, X. Feng, K. Muellen, A. C. Ferrari, C. Casiraghi, and D. Prezzi, Raman fingerprints of atomically
precise graphene nanoribbons, NanoLett, 16, 3442 (2016)
Z. Chen , W. Zhang, C.-A. Palma, A. Lodi Rizzini, B. Liu, A. Abbas, A. N. Richter, L.
Martini, X.-Y. Wang, N. Cavani, H. Lu, N. Mishra, C. Coletti, R. Berger, F.
Klappenberger, M. Kläui, A. Candini, M. Affronte, C. Zhou, V. De Renzi, U.delPennino, J.
Barth, H.J. Räder, A. Narita, X. Feng, and K. Mullen, Synthesis of graphene nanoribbons by
ambient-pressure chemical vapor deposition and device integration, J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
138, 15488 (2016)
|
|
|
|
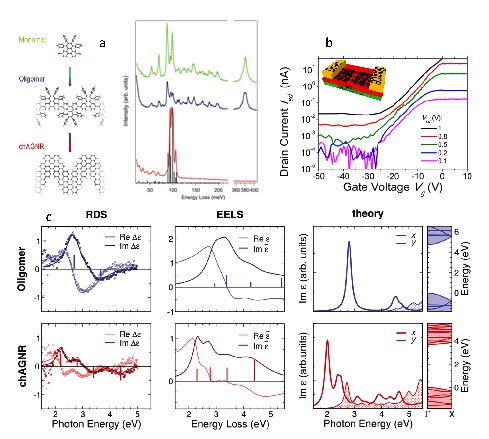
The use of different spectroscopies-ranging from
EELS and RDS to femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy-, in combination with
theoretical simulations including many-body effects, allows us to elucidate the nature of
optical excitations, demonstrating the fundamental role played by excitons and biexcitons in
determining the linear and ultrafast optical response of GNRs.
G. Soavi, S. Dal Conte,
C. Manzoni, D. Viola, A. Narita, Y. Hu, X. Feng, U. Hohenester, E. Molinari, D. Prezzi, K.
Muellen, and G. Cerullo Exciton–exciton annihilation and biexciton
stimulated emission in graphene nanoribbons, Nat. Commun , 7,
11010 (2016)
R. Denk, A. Lodi-Rizzini, S. Wang, M. Hohage, P. Zeppenfeld, J. Cai, R. Fasel, P. Ruffieux,
R. F. J. Berger, Z. Chen, A. Narita, X. Feng, K. Müllen, R. Biagi, V. De Renzi, D. Prezzi,
Alice Ruini and A. Ferretti Probing optical excitations in chevron-like
armchair graphene nanoribbons, Nanoscale , 9, 18326 (2017)
|
|